
Whether it is an internal corporate application, or a client application used by millions of customers, by rule of thumb, the product needs to be compliant with the WCAG guidelines. As part of the Xoriant UX team, in this blog, we will uncover key reasons why it is important to have your product accessible to as many users as possible, highlight the takeaways, and understand the processes and steps necessary to make a product accessible.
Accessibility: The Ability to Access
A common misconception often assumed by product companies is that accessibility is about disability. It is not. It is about universal design.
Imagine if 95% of the websites or mobile applications we use today lock us out. Whereas everyone else continues to experience the convenience of mobile banking and the freedom of online shopping, but for you, they’re inaccessible. Wouldn’t that be biased and unfair?
On a global scale, around 15-20% of people on the planet identify as specially challenged. And more than one in five Americans are specially challenged.
Whom Does Accessibility Help?
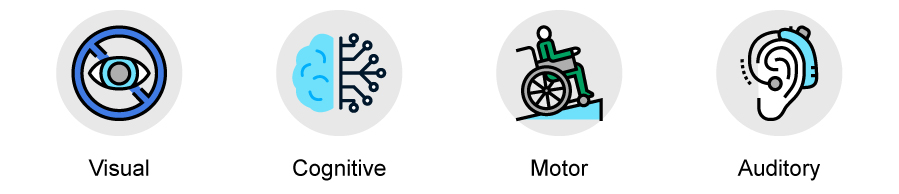
Accessibility helps users experiencing reduced visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive abilities. The impaired users rely on various assistive technologies and alternate methods of interaction to access. It can be websites, mobile applications and much more.
Users with visual impairments including blindness, low-level vision, and color blindness may rely on screen readers such as Braille displays, zoom functions or a high contrast color to get value what’s displayed on the screen.
Users with auditory disabilities rely on captions or transcripts for accessing video content.
Users with motor disabilities might require speech-to-text software, or keyboard-only interactions.
Users with cognitive disabilities often require a thoughtful and organized layout with clear direction .
Specially challenged people rely on various assistive technologies and alternative methods of interactions with any products.
Accessibility Aided-Technologies & Software
There are various technologies and software that enable specially challenged users to access applications and software. Some of the prominent examples of accessibility aided technologies and software are as follows:
Assistive Technology: An example of assistive technology is closed captioning in videos.
Magnification Devices: This type of device is used by low vision users for appropriate reading experience.
Screen Reader: This technology reads the content of the screen to the users.
How to Build Accessible Websites or Apps?
According to a Law firm’s report, in 2020, more than 10,982 lawsuits were filed for ADA Title III in federal courts in the US.
Building accessible websites or apps can be tricky without the right guidance. Software engineering teams including Developers, Testers, App Owners, and Accessibility Experts from around the world rely on these standards for proper accessibility testing direction. In fact, many US federal government agency sites and apps are required by law under Section 508 to be accessible. This law includes the WCAG standard.
Demystifying WCAG
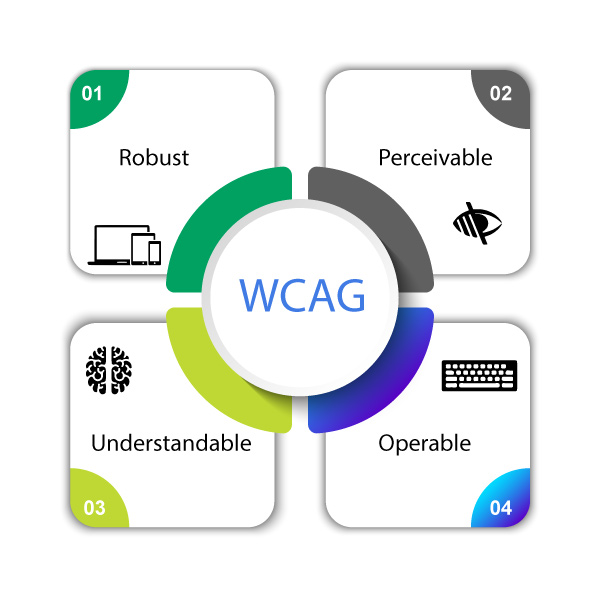
The Web Content Accessibility Guideline or WCAG, published by the W3C (World Wide Web Consortium), is the standard rule set that defines what makes a site accessible. WCAG is built around four core principles: POUR
Perceivable: All visitors must have a similar experience regardless of their ability. For example, people must be able to comprehend the content either by seeing it or hearing it.
Operable: All the controls and interactive elements must be usable. For example, people must be able to use the computer by typing, or by using voice as an input type.
Understandable: Content must be clear, mitigating confusion and ambiguity. For example, people must be able to comprehend with a clear and simple language.
Robust: Content must be accessible with a wide range of technologies. For example, people must be able to use different assistive technologies.
The WCAG outline three levels of accessibility standards - A, AA, AAA
- Level “A” is essential for Universal Design.
- Level “AA” provides enhanced accessibility and includes or enhances level A requirements. This is the level a company must target for the website and application projects.
- Level “AAA” is the highest level of accessibility and includes or enhances both A and AA requirements.
Design Planning
Visual Design: In the visual design stage, you must think about good color contrast. So that users with low vision can read what’s on the screen or on the page.
Interaction Design: When you’re thinking about interaction design, you want to ensure that where the keyboard users that only use a keyboard can complete all of the tasks that they’re typing to achieve.
Color Contrast
Color contrast is a ratio of contrast between two things to be accessible. There should be adequate contrast between the color of a piece of information in the foreground and the color of its background.
Never Depend on Color Independence
Error: Use appropriate color to highlight or complement what is already visible. If you see below example, you will see the difference in Signup screen Before and After accessibility is applied. This type of solution helps people with visual impairment for better navigation.
Graphs: When displaying elements such as graphs or charts, giving users the option to add texture or patterns ensure that those who are color-blind can distinguish between them without having to worry about the color affecting their perception of the data.
Progress Tracker: Try to incorporate different shapes and color contrast while designing progress tracker. It helps user to identify easily at what step they are on in the progress bar.
Conclusion
Accessibility means treating everyone the same with equal opportunities - no matter their ability or circumstances. It helps user to experience the same user interface despite being their disability. Accessibility is the concept of whether a product or service can be used by everyone. Making your products, websites and applications accessible benefits individuals, businesses, and society.
With new releases and interfaces coming to market every day, are you struggling to deliver a seamless, intuitive, and consistent user experience while being WCAG-compliant? At Xoriant, our expert UX teams stay ahead of the user experience curve by investing in the latest research and next-gen technologies to help your team exceed customer and market expectations.






 View Previous Blog
View Previous Blog