
Bitcoin, Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology
Blockchain has proved its capability to be one of the strongest emerging technologies with expected global revenue growth of $23 million by 2023. It is expected to be adopted widely across industries powered by its decentralized structure and the strong security measures that can get rid of major flaws in business models.
Bitcoin has played a major role in making Blockchain and the distributed ledger technology systems famous. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) prevalent even before blockchain, is a database of records that are not stored or confirmed by any one central authority, but, is distributed across multiple organizations.
On the other hand, a blockchain is a form of a distributed ledger with a very specific technological concept which cryptographically creates an immutable ledger of records. It is maintained by a decentralized network where all records are approved by consensus.
The Current State of Blockchain
The blockchain world has branched into two major categories – Public blockchains and Private blockchains. Public blockchains with associated cryptocurrencies have experienced remarkable fame incentivizing and rewarding participants in the network, making them multi-millionaires. However, they have also witnessed a downfall due to hidden loopholes. On the other hand, the use of permissioned / private / enterprise blockchains has been growing steadily witnessing major capabilities since 2017 with live deployments across multiple industries.
For enterprise blockchain, one must ensure fool-proof technology considering implementation and easy adoption to changing business models. Most of the enterprise blockchain use cases are built across banking, trade, finance, supply chain, healthcare, etc. The sole purpose of moving to a blockchain-based solution is to deliver an immutable, irreversible, distributed, resilient, and non-centralized ledger system. Making the solution secure, tamper-proof and safe of exceptions becomes a vital challenge.
With immense potential, market demand and developer community building frameworks and solutions, enterprise blockchains are gaining traction. Choosing the right blockchain framework pertinent for your business use case for faster and stable delivery is a crucial step for enterprises before initiating a blockchain project. This decides the favorable outcome or repercussions entailing large businesses and customers.
Today, through this blog, we bring to you R3’s Corda - a blockchain and DLT framework emerged as a need for financial institutions. With a clear understanding of DLT and Blockchain, Corda is used to maintaining transactions on a trusted non-centralized ledger. R3’s Corda is built majorly considering a distributed system with the combination of various blockchain features such as preserving privacy, identity, business model, and consensus of the distributed network. With the help of these features, we would introduce Corda demonstrating how this framework is unique from other blockchain frameworks.
Overview of R3 Corda
R3 is a consortium that started on September 15, 2015, with the world's leading financial companies. Today, the consortium has outgrown into an ecosystem of 300+ members actively contributing to the field of Blockchain and Distributed ledger technology.
R3 decided to leverage the power of blockchain technology to solve real business problems in both multifaceted and highly regulated business markets. Recognizing that there wasn’t a blockchain framework in the market that could serve their purpose, R3 built one from scratch and named it “Corda”.
“Corda is an open-source blockchain project, designed for business from the start. It allows you to build interoperable blockchain networks that transact in strict privacy. Corda's smart contract technology allows businesses to transact directly, with value.”
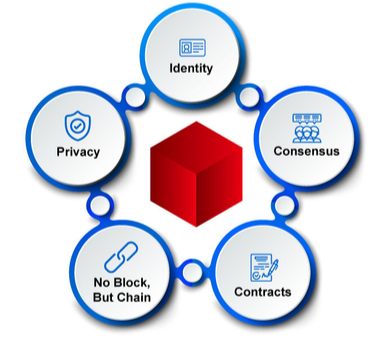
What Makes Corda Blockchain Framework Different?
Privacy: Privacy is a critical focus for any distributed ledger technology system. It is because your data is bound to be distributed across multiple nodes and servers belonging to different business entities. In R3’s Corda, the only parties who have access to the details of a transaction are those involved in the transaction and those who need to assure themselves of transaction provenance.
It means two or more participants can transact with one another, sharing only necessary information between them. This is in stark contrast to public blockchain or few private blockchain frameworks - broadcasting the transaction or its details across the entire network. The privacy feature of the Corda blockchain framework is what enterprises and businesses would want. Like other comrade frameworks, Corda does not include any gossip protocols which broadcasts all transactions to the network.
Identity: Identification of different parties in the DLT system over a permissioned blockchain becomes a core criterion to build a closed network of the system among known participants. In R3 Corda, parties have assurance over the identity of members in the blockchain network.
Identity is a very important feature for a global decentralized ledger where you are unaware of other participants. It is made possible with KYC requirements of all participants across the network and the core identity framework which enables Corda to assign a single user profile to any legal entity, be it an organization or an individual.
Consensus: Consensus is a technique through which organizations over a distributed and decentralized network come on to an agreement over the transactions happening between them. It is an important concept to identify malpractices and maintain the integrity of any blockchain network, no matter if its public or permissioned.
Transactions in Corda are confirmed through a process of consensus using a variety of algorithms, including Byzantine Fault Tolerant algorithms. Just like any other blockchain, the unique features a Corda network can support multiple different consensus pools using different algorithms enabling its clients with a pluggable consensus model based on their requirement.
Contracts: Smart contracts and program files embedding the business logic, rules validation are part of any business being run among different organizations over a blockchain-based distributed system. In R3’s Corda, transactions are processed by having each participant execute the same code deterministically to verify the proposed updates to the ledger.
Just like Ethereum, the languages you can use are high-level and productive, like Java and Kotlin, rather than obscure ones like Solidity. The validation function of the CorDapp (Corda Distributed Applications) contract code only needs the validation chain of each associated transaction.
No Block, But Chain: Corda’s functionality relies on the UTXO input/output model, which is very similar to the transaction system used in traditional blockchains such as Bitcoin. However, the storage and verification do not end up into a chain of blocks like other enterprise blockchain frameworks, e.g., Hyperledger Fabric that bundles up a set of transactions between ‘n’ number of participants over the channel into a block-based on different criteria. Corda links transaction in a cryptographically linked (chained) chain to the transactions it depends on and not to a previous block of some other set of transactions.
Next Steps
Unlike various enterprise blockchain platforms mentioned above, Corda does not periodically batch up transactions based on some criteria, awaiting confirmation into a block and confirm them in one go. Instead, R3’s Corda confirms each individual transaction in real-time.
There is no need to wait for a bunch of other transactions to tag along or wait for a “block interval”. Each transaction is confirmed as we go. As Corda supports multiple notaries on the same network, this massively increases privacy, enables things to move faster and smoother.
Corda is an enterprise framework that deeply understands the idea behind a DLT and blockchain technology. It is flexible enough to fit into a variety of industry use cases, making it an ideal blockchain framework without including chains or cryptographic blocks.
At Xoriant, we actively explore various blockchain frameworks to build solutions for clients across various industry verticals. We guide your approach to blockchain investment with the experience and expertise of working across different blockchain frameworks and identify the right opportunities for you. Thus, providing you with a blockchain solution with minimized risk, effort and high capability.
Want to know how Xoriant can help you with your Blockchain Projects?






 View Previous Blog
View Previous Blog